The Hidden Environmental Cost of Animal Agriculture
Did you know that animal agriculture accounts for 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, more than the entire transportation sector combined?
This startling statistic (FAO) highlights just how much our dietary choices impact the planet. While driving less or switching to renewable energy are often seen as the go-to strategies for reducing carbon footprints, rethinking what’s on our plates can be an equally, if not more, effective way to combat climate change.
In this post, we’ll uncover the environmental toll of animal agriculture, from its impact on greenhouse gas emissions to resource depletion and biodiversity loss. By understanding the scope of the problem, we can take meaningful steps toward a more sustainable future.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Closer Look
Animal agriculture is a significant contributor to global warming due to the release of methane, nitrous oxide, and carbon dioxide. Here’s how it breaks down:
Methane from Livestock: Cattle and other ruminants produce methane during digestion, a greenhouse gas 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide (ERA).
Manure Management: Animal waste generates both methane and nitrous oxide during storage and treatment (EPA, 2020).
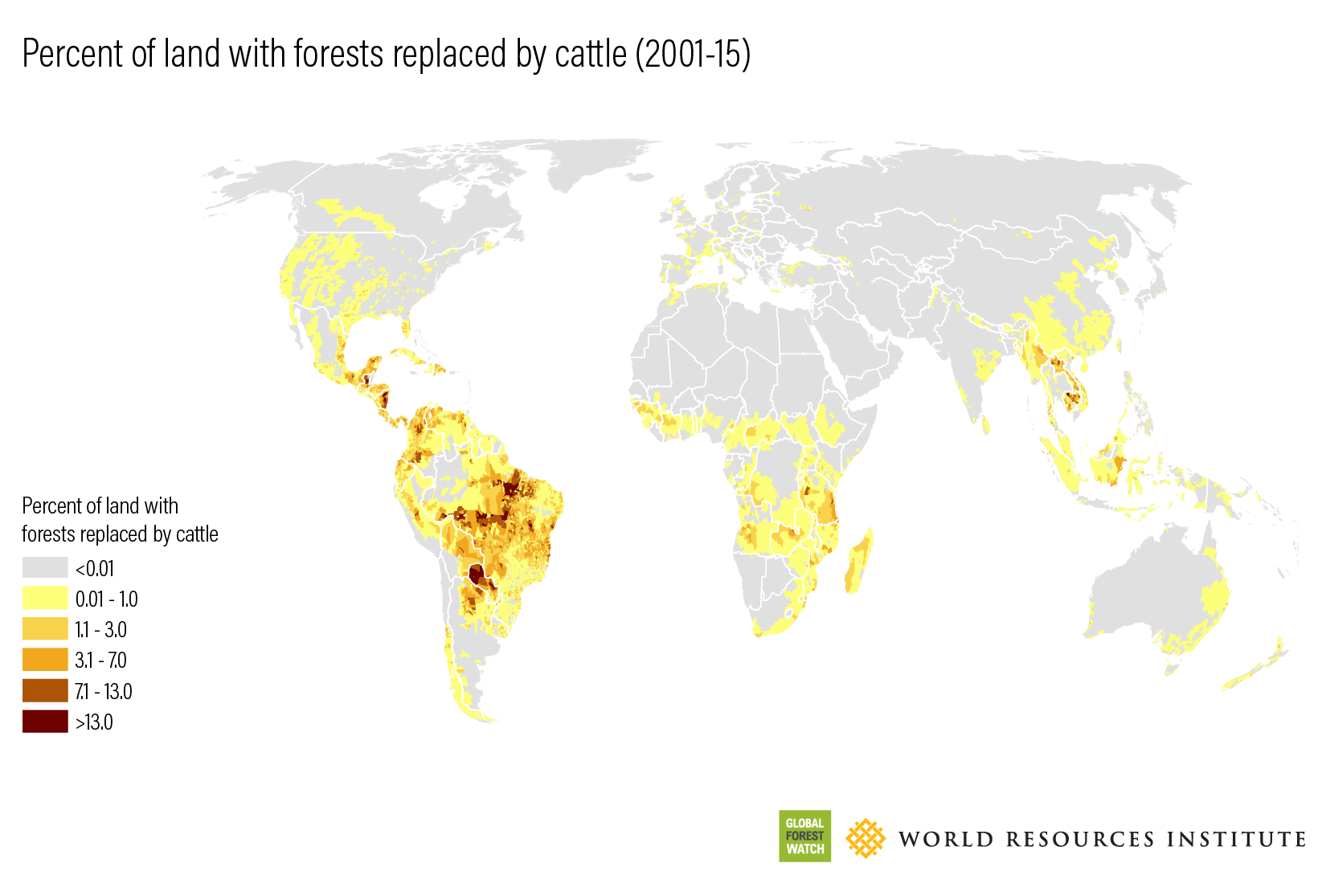
Deforestation: Forests are cleared to create grazing land or grow feed crops, releasing stored carbon dioxide into the atmosphere (WWF, 2021).
Key Statistic:
Producing one kilogram of beef emits 60 kilograms of CO2-equivalent gases, compared to just 2.5 kilograms for legumes (OWiD).
Resource Depletion: Land, Water, and Energy
Animal farming is one of the most resource-intensive industries. Consider these impacts:
Land Use: Livestock requires extensive grazing areas, contributing to deforestation and habitat destruction. Nearly 80% of global agricultural land is used for livestock, yet it provides only 18% of calories consumed by humans (FAO, 2018).
Water Consumption: Producing a single pound of beef requires approximately 1,800 gallons of water, compared to 119 gallons for potatoes or 216 gallons for tofu (Mekonnen & Hoekstra, 2012).
Energy Demands: Growing crops for animal feed consumes significant amounts of fossil fuels, fertilizers, and pesticides (CIWF, 2021).
Source: culinaryschools.org
Biodiversity Loss and Ecosystem Disruption
Animal agriculture isn’t just about greenhouse gases and resource use; it’s a leading driver of biodiversity loss.
Deforestation for Grazing: Large swaths of rainforests, especially in the Amazon, are cleared to make room for cattle ranching (Greenpeace, 2020).
Pollution: Runoff from animal farms pollutes rivers and oceans, creating dead zones where marine life cannot survive (National Geographic, 2021).
Species Extinction: Habitat loss directly contributes to the decline of countless species, including jaguars, orangutans, and countless bird species (IUCN Red List, 2020).
By shifting to a plant-based diet, you can help preserve biodiversity and protect vital ecosystems for future generations.
What Can You Do?
If this sounds overwhelming, don’t worry—every small step counts! Here are actionable ways to make a difference:
Start Small: Try Meatless Mondays or swap one meal per day with a plant-based alternative.
Educate Yourself: Watch documentaries like Cowspiracy (2014) or Seaspiracy (2021) to learn more about the environmental impacts of animal agriculture.
Track Your Impact: Use tools like a carbon footprint calculator (Nature Conservancy) to see how dietary changes can reduce your emissions.
Conclusion
The environmental toll of animal agriculture is immense, but the solution is within reach. By making conscious choices, such as reducing or eliminating animal products from your diet, you can significantly decrease your carbon footprint, conserve resources, and protect biodiversity.
Challenge for Readers: Try one plant-based meal this week and use a carbon footprint calculator to measure your impact. Share your results in the comments below—we’d love to hear about your journey toward sustainable living!